

Keywords
Renewable Energy, Power Sector, Sustainable, Climate Change, Solar Power, ARC Advisory Group.
India’s growth story is powered by its energy sector. Efforts are on to reduce the dependence on finite, polluting fossil fuels and shift to renewable and clean sources of energy for sustainable development. Renewable energy reduces greenhouse gas emissions, improves energy security, and provides energy access to remote villages. To accelerate the transition to a more sustainable energy future, all stakeholders in the value chain must collaborate to mitigate the negative impacts of climate change and ensure a better future for all.
At COP-21 in Paris in 2015, India committed to a 40 percent share of power generation from non-fossil fuel sources, and this target has already been achieved. Today, India is the world's fourth largest country in installed capacity of renewable energy (including large hydro). The government has implemented various policies and initiatives to support renewable energy development. These include financial incentives, tax benefits, and competitive bidding processes for project allocation. The government is also attracting domestic and foreign investments in the renewable energy sector.
India’s continued industrialization and urbanization will make huge demands for reliable and sustainable energy. The country’s commitment to renewable energy development, supported by favorable policies, targets, and investments, augurs well for this sector. This Insight provides an overall view of India’s energy transition, with a particular focus on solar power.
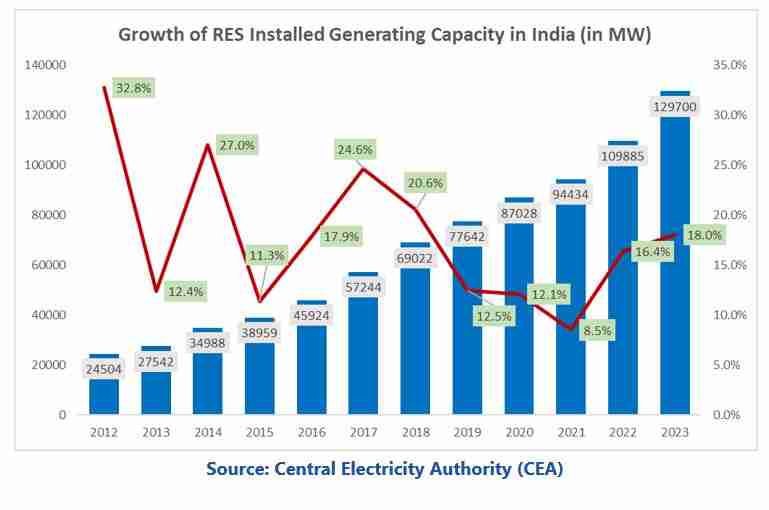
India has been taking significant steps to transition towards cleaner and more sustainable sources of power. As of March 31, 2023, India’s installed renewable energy (RE) capacity (excluding large hydro) stood at nearly 130 GW, representing about 31 percent of the overall installed power capacity. Solar power is estimated to contribute 66.8 GW, followed by 42.6 GW from wind power, 10.8 GW from biomass, 4.9 GW from small hydropower, 4.8 GW from pumped storage projects (PSP).
Solar Power: Solar power has been a major focus of India's renewable energy development. The country has experienced significant growth in solar capacity and is expected to continue expanding its solar power generation. India has implemented initiatives such as the Jawaharlal Nehru National Solar Mission (JNNSM) to promote solar energy adoption. Launched in 2010, the Mission aims to promote ecologically sustainable growth while addressing India’s energy security challenge.
Wind Power: India has abundant wind resources, particularly along its coastal areas. India has been harnessing wind energy through onshore and offshore wind projects, and it aims to significantly increase its wind power capacity in the coming years.
Hydro and Bioenergy: While solar and wind energy have been at the forefront of India's renewable energy efforts, the country also recognizes the importance of hydroelectric and bioenergy sources. India has been exploring the potential of small hydropower projects and is promoting the use of biomass and biogas for energy generation.
As the renewable energy capacity increases it becomes critical to integrate energy storage systems and grid infrastructure. The government has been focusing on developing energy storage technologies and implementing smart grid solutions to facilitate the smooth integration of renewable energy into the power grid.
India is blessed with abundant sunlight, which can effectively be harnessed to meet the country’s power requirements. Approximately, 5,000 trillion kWh per year of solar energy is incident over India's land area with most parts receiving 4-7 kWh per sq.m per day. Solar energy based decentralized and distributed applications have benefited those in rural areas by meeting their requirements for lighting, cooking etc. in an environmentally friendly manner. The social and economic benefits include:
ARC Advisory Group clients can view the complete report at ARC Client Portal
If you would like to buy this report or obtain information about how to become a client, please Contact Us
Learn more about ARC In-depth Research at Market Analysis
Learn more about ARC Strategic Services at Advisory Services for Industry Leaders

