

Despite the application of a wide variety of safeguarding measures, many accidents in the process industries continue to occur. Experiences gained from past accidents have led to the development of an increasing number of technical solutions. One of the best known and widely accepted technical solutions concerns the use of safety instrumented systems (SIS). To control the design and implementation of these technical solutions, numerous safety-related standards have emerged. These standards consist of technology-oriented requirements defining “adequate” implementation of the designed solutions. Consequently, compliance with these standards is often considered to be “good engineering practice.” Compliance with these technical standards, however, did not prevent several major accidents. Because of the growing complexity of both industrial processes and the related SIS, new challenges have arisen including how to better manage safety systems.
Safety lifecycle management in general continues to be a big issue in process plants, driven largely by the need to conform to current standards and best practices like ISA 84 and IEC 61511. The primary goal of these standards and practices is to develop a continuous improvement approach to safety system management and ease the burden on end users so they better understand the safety status of their assets and can act appropriately.
Recent updates to the standards highlight the need to focus on the total safety lifecycle, confronting the myth that once a system is designed no further effort is required on the part of the end user. On the contrary, the work has just begun and end users are poorly prepared overall to address the safety lifecycle as called upon by industry best practices.
In a nutshell, the process safety lifecycle describes a safety instrumented system’s (SIS) life and the activities around it from conception through retirement. IEC defines the lifecycle using a flow chart within the 61511 standard (Ref figure below). ISA 84 effectively mirrors the IEC standard. The standard is a set of knowledge and experience from past projects, and bring considerable benefits if applied properly.
IEC 61511 use the safety lifecycle as a framework and define a series of phases:
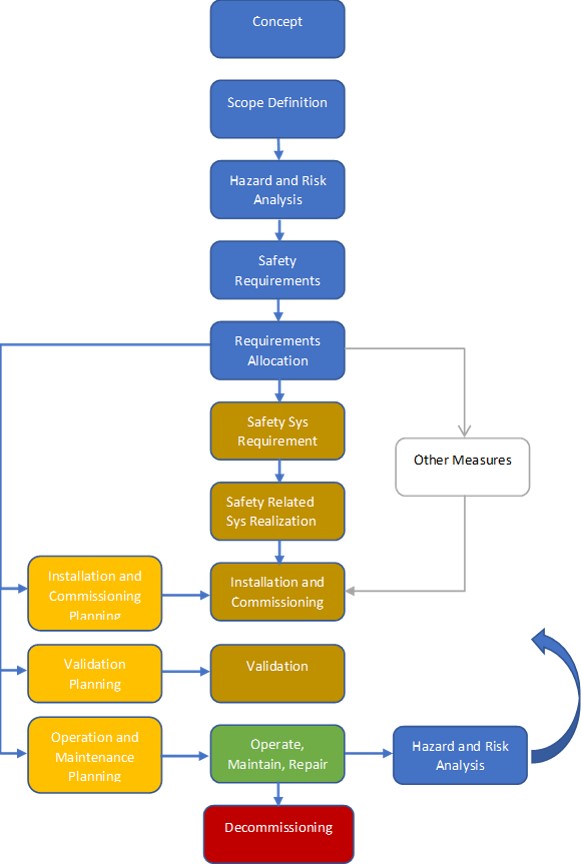
Phase 1: Hazard and risk assessment
Phase 2: Allocation of safety function to protection layers
Phase 3: SIS safety requirements specification
Phase 4: SIS design and engineering
Phase 5: SIS installation, commissioning and validation
Phase 9: SIS verification
Phase 10: Management of functional safety and functional safety assessment and auditing
Phase 11: Safety life-cycle structure and planning
Every phase has a set of inputs and outputs, at the end of each phase a verification process shall be performed to confirm the required outputs are as planned.
Some of the benefits to implement correctly IEC 61511 standard are:
Avoid SIF over-engineered / under-engineered
Improved safety
Reduce downtime
Cost-effective systems and maintenance processes
Compliance with safety authorities’ regulations.
Not surprisingly, process safety lifecycle management is the management of the safety processes to ensure that the safety processes operate as intended over its effective life. It is an integral part of a successful enterprise risk management program. A proper lifecycle management system ensures that adequate planning exists (or is developed) that makes certain that the safety instrumented system shall meet the safety requirements and demonstrates by review, analysis and/or testing that the required outputs satisfy the defined requirements for the appropriate phases of the safety life cycle identified by the verification planning.
Several vendors offer a variety solutions to aid end users in managing their systems. These solutions help users prove compliance with regulations and standards and provide a status of overall risk. The solutions will also help identify problem areas.

