


This is a main reason why operations and maintenance teams seek solutions that can help them harness the power of data to make critical decisions as quickly and accurately as possible and at the point of work. This is consistent with their primary goals to enhance operations performance, reduce downtime, and maximize overall return on assets.
While today’s industrial organizations have much data on hand, often there is a dearth of timely, relevant, readily accessible and actionable information. Now more than ever, maintenance and operations teams need tools to help them assess operations performance so they can make critical decisions safely, in real time, and at the actual point of work.
Maintenance teams continue to seek ways to improve their ability to collect and interpret meaningful information from all the data generated from disparate IT/OT systems. Their quest includes ways to effectively track and manage inspections and maintenance processes. While traditional maintenance software have long been used to document the work done, expectations are now much higher and must cater proactively to the next-gen workforce.

Due to the labor-intensive nature of these industrial organizations, to realize these capabilities it’s now essential to enable the field worker through technology.
For daily operations, field workers need visibility into equipment health and performance, quick access to other relevant information, and the ability to trigger the right actions. During repairs, these include visibility into the issue, probable causes, recommended actions, and parts requirements and availability.
These capabilities are necessary due to the wide variety of data now available from operations and maintenance systems along with IoT data. Examples include parts and labor time, costs, sensor inputs, and the workflow rules typically generated when managing and maintaining complex assets. Consequently, organizations are searching for ways that these data can be collected, massaged, and leveraged for decision making at the point of action.
Today’s wearable devices provide an effective way for field workers to visualize and consume actionable information. Interest in wearables is building for a variety of reasons, including fast data capture, hands-free operations, and remote monitoring and assistance. These tools can be particularly valuable in areas such as maintenance inspections, simulating hazardous field conditions, diagnosing faults, planning work, and displaying repair instructions. They can help reduce inspection times and improve inspection accuracy. Moreover, they can be useful for designing and providing training in a controlled environment. This can increase knowledge retention, reduce travel costs, and improve training productivity.
With the current availability of intrinsically safe wearables, it is now possible to enable maintenance technicians and other field workers in hazardous working environments with context-specific information in near real-time at the point of repair. This can be accomplished using a wide variety of tools and mobile devices. Examples include smart glasses, head-mounted displays using augmented reality for inspection and remote expert assistance, mixed reality for collaborative planning, and virtual reality for training. In addition, smart watches and other wearables can be used to track the physical locations of workers and monitor their health.

Smart glasses and similar variants can display detailed asset information, instructions, schematics; show illustrated images and drawings; and allow communication with remote subject experts - all from on-site. Heads-up or head-mounted displays are sometimes employed.
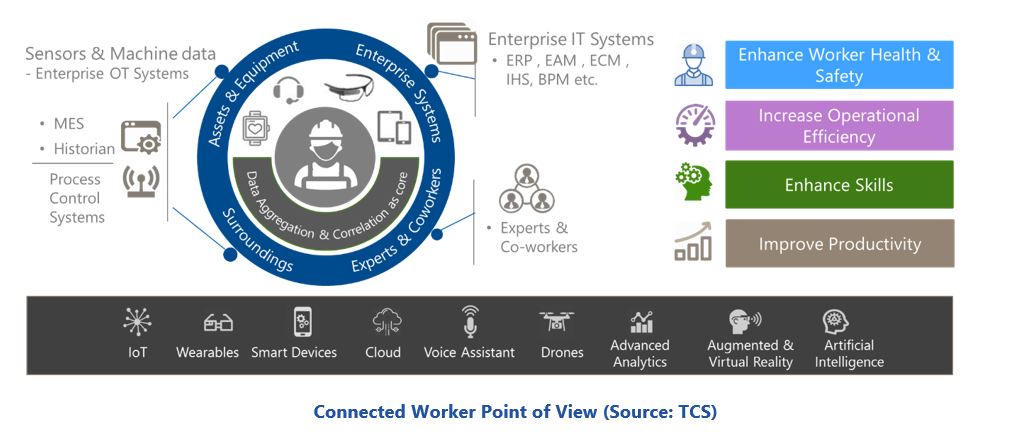
The TCS Connected Worker solution has been designed specifically to accelerate adoption of digitalization by field workers and enhance real-time operational visibility across the organization. According to TCS, it also supports in-field, data-driven decision making by providing field workers with real-time contextual information from various OT and IT systems and enables information to be shared in real time.
The TCS Connected Worker solution helps bring digital transformation down to the field level. It was designed to address the requirements of the industrial worker and offer a scalable ecosystem for use cases such as health and safety, operational efficiency, productivity improvement, and skill enhancement.
According to TCS, this offering delivers end-to-end connected worker solutions by leveraging the company’s cross-industry expertise across engineering services, IoT, and digital technologies coupled with an ecosystem of alliances and partners. Some of the key benefits of this solution include:
Being able to assess equipment operation and health on the shop floor or in the field and managing worker effectiveness and productivity are major contributors to highly functioning maintenance and operations teams. A connected worker solution that supports these capabilities (typically augmented by equipment information from sensors, enterprise IT/OT systems and IoT devices), can elevate maintenance effectiveness significantly.
Examples of potential benefits include reduced maintenance and repair costs and higher labor efficiency and productivity. Ultimately, this can result in increased profitability and return-on-assets for companies embracing a connected workforce strategy.
ARC Advisory Group clients can view the complete report at ARC Client Portal
If you would like to buy this report or obtain information about how to become a client, please Contact Us
Keywords: Connected Workforce, Operations, Maintenance, Contextual Information, Actionable Insights, IoT, Wearables, TCS Connected Worker, ARC Advisory Group.

