

Part Two of this article features more stories of end user Industrial IoT adoptions and digital transformation journeys from the recent Industry of Things World Asia conference in Singapore, which this year was chaired by ARC Advisory Group. As mentioned in Part One, hearing from other end users on their motivations, experiences and challenges can be a powerful learning step for companies looking to initiate and move forward with projects in these areas.
Blasting out rocks in underground mines is not something that usually comes to mind when thinking about IoT, but it is a technology that Australia’s Orica, the world’s largest supplier of commercial explosives and blasting systems to the mining, quarrying, oil & gas and construction industries, is adopting to improve the productivity of its customers’ blasting operations. What the company calls Digitally Enabled Better Blasting becomes possible through Orica’s BlastIQ Platform, which incorporates a range of technologies to provide data-driven benchmarks and insights needed to ensure sustainable, cost-effective improvements in blast performance.
The technologies include IoT sensors for getting an understanding of the resource via real-time geoscience capability and for measuring vibration, noise, air-blast, temperature, humidity, wind, dust and other parameters associated with the blasting operation itself. For post-blast fragmentation measurement, Orica’s FRAGTrack is a binocular image capture system that provides blast fragmentation data with auto-analysis capability. The data can be related to blast designs and loading information, enabling matching and optimisation of outcomes to inputs. And ORETrack provides RFID based tracking of rock movement from the blast. The rugged RFID tags survive the blast, and the system provides automatic alerts when undesired material such as contaminated ore enters the plant.
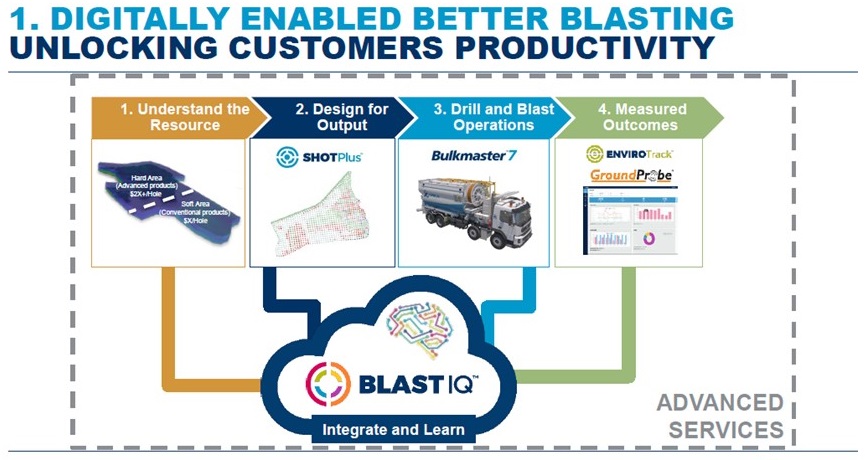
Like Buhler Aeroglide featured in Part One of this article, Orica’s story is very much about evolving a product-centric company towards a product + enhanced services business enabled by Industrial IoT. As the company neatly articulates: “Manufacturing and distributing explosives is hugely expensive, and margins on our products are diminishing. To meet growth expectations we must identify new sources of revenue. These will come in the form of digital technologies, novel business models, and entirely new lines of service that come of the back of our IoT platform.”
While correctly perceived as one of the world’s largest industrial automation companies with an array of global manufacturing clients, less well known is the fact that Rockwell Automation is a significant manufacturer in its own right, with its 20 plants around the world producing everything from pushbuttons, LED signal lights and sensors right up to drives, PLCs and motor control centers.
Its drive to undertake digital transformation in its own facilities came from the realization that many plant decisions were being made based on gut feeling, experience, and tribal knowledge rather than hard data. While manufacturing data was available, a heavy reliance on manual entry into spreadsheets meant it took days to understand what happened on the shop floor and even longer (weeks) to understand why a particular incident, such as incorrectly inserted electronic components, occurred. Further, where more sophisticated applications were in use, these were proprietary to particular plants, making it difficult to gain an overall view of manufacturing operations performance.
Enter the Connected Enterprise. This is Rockwell Automation’s approach to enabling the Industrial Internet of Things by converging plant-level and enterprise networks via its Integrated Architecture technology and using information solutions capabilities such as scalable analytics and mobility/collaboration to enable better and faster decision making based on a seamless connectivity to the shop floor.
What it means on a practical level for Rockwell global manufacturing is clear visibility – through remote dashboards – into each of the operations at the 20 plants and the ability to compare and contexualize data such that best practices can be identified for replication in other facilities.
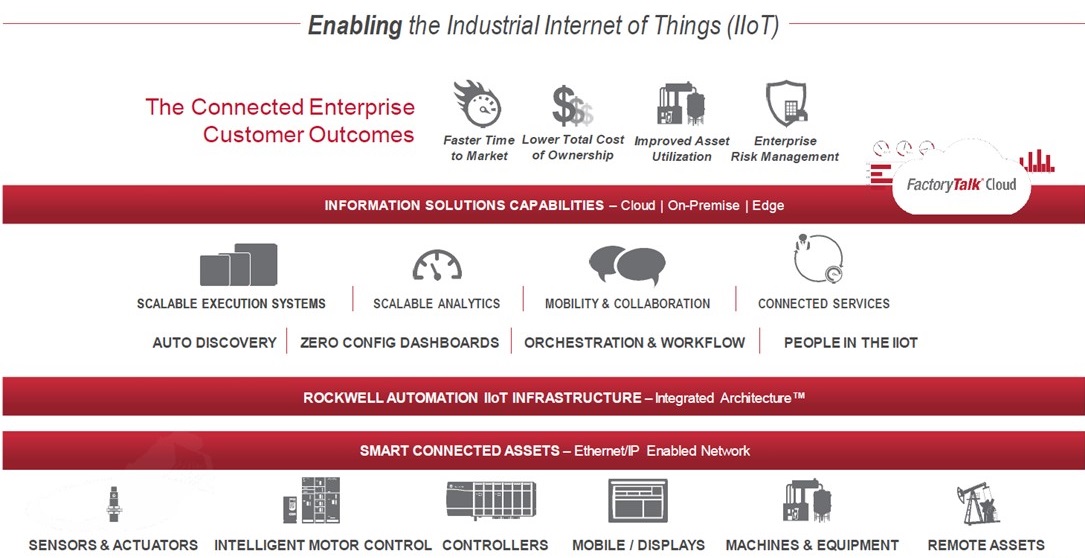
The results from Rockwell Automation’s internal Connected Enterprise initiative, which remains an ongoing journey and increasingly incorporates advances such as predictive analytics for, for example, early detection of SMT-machine nozzle defects, are impressive and include: product quality improvement through ppm defect reduction by 50 percent; 30 percent reduction per year in capital expenditure through capital avoidance; lead times reduced by 50 percent; and on-time customer deliveries up to 96 percent from the mid-80 percent range. Externally, Connected Enterprise is a key offering to the company’s customers, with the likes of BHP Billiton, Ford and Shell all realizing benefits in quality, productivity and reliability.
This steel products supplier to the building and construction industry identified four drivers of its digital transformation initiative: the need to maintain margins in a competitive industry by boosting productivity, quality and agility; evolving customer and internal stakeholder expectations; major shifts in available and applicable technologies; and new business models rapidly disrupting the global steel industry.
To focus the digital transformation, NS Bluescope, a 50/50 joint venture enterprise between Bluescope and Nippon Steel & Sumitomo Metal Corporation of Japan, concentrated on three aspects of value proposition: Customer Experience – with aspects such as improving customer understanding through analytics-based segmentation and increasing top line growth through predictive marketing and digitally enhanced selling; Operational Process – including digitizing processes to realize performance improvements and enabling workers to work from anywhere/anytime and with greater knowledge sharing; and Business Model – digitally modifying businesses through aspects such as product/service augmentation and launching new digital businesses via digital product development and reshaping organizational boundaries.
And to undertake its digital transformation, which is currently ongoing, NS Bluescope adopts a structured, six-step approach:
• Digital Maturity Assessment – obtain a deep understanding of the current state of digitization in the organization
• Identify Opportunities and Threats – ascertain customer demands, competition dynamics, and digital best practices across all business domains
• Define Digital Vision – top-down definition and communication of the digital vision and with an agenda that caters for long and short term objectives
• Prioritize Transformation Domains – select what to do first based on likely business benefits and ease of implementation
• Derive Digital Roadmap – the transformation journey outlined in a phased roadmap
• Implement and Sustain – the change process is implemented across the transformation domains
Aside from the six companies featured in these two articles I should mention there were many other manufacturers from a variety of industries usefully articulating their experiences at this year’s Industry of Things World Asia: 3M, Apollo Tyres, CITIC (China), Continental, Cummins, EMD Millipore, Fonterra, India Glycols, Maynilad Water Services (Philippines), Merck, Mondelez International, Monsanto, Petronas, Procter & Gamble, Supreme Industries (India), ThyssenKrupp, XCMG (China). The event returns to Singapore next year (July 10-12) and I for one certainly look forward to hearing more interesting stories from end users over at the cutting edge of Industrial IoT and digital transformation.

