

The TATA Consultancy Services (TCS) Utilities Business Unit recently briefed ARC Advisory Group on its image analytics capabilities. Specifically, Sumitkumar Ray, Chief Technology Officer; Anindya Pradhan, 
The program, named “Machine Vision,” was developed at TCS research and Innovation under the leadership of Mahesh Rangarajan, Enterprise Architect, and Dr. Jay Gubbi, Senior Scientist. TCS research on machine vision capabilities is targeted at building intellectual property on imaging datasets in a variety of spectrum bands and creating artificial intelligence/machine learning (AI/ML) algorithms. This includes capabilities to process visual RGB (streaming or otherwise), thermal, infra-red (IR), near infra-red (NIR), multi-spectral and hyper-spectral datasets.
The TCS Machine Vision solution focuses on three core themes:
TCS thus plays in the full ecosystem of image analytics. Examples include determining the flight paths of UAVs, actual flight control; capturing images, automated validation and rejection; ingesting, storing, and processing data; automated annotation and damage detection; integration with landscape and predictive/prescriptive analytics with conflated data (structured and unstructured).
Applications can combine and analyze imagery from multiple sources to assess and predict conditions for vegetation to encroach upon overhead lines and towers in transmission & distribution, distributed generation, and other utility-related applications. It can also use image analytics to automatically identify damage to different field assets. At the back end, TCS highlighted the need to integrate the data platform it has developed in Machine Vision. This new data platform can consume, combine, and manage petabytes of both unstructured image data and structured enterprise data.
The company’s approach uses proactive, condition-based monitoring with image analytics to enhance asset life and improve both grid reliability and the operating efficiency of distributed energy resources (DER).
TCS’ approach to image analytics includes the use of contextual knowledge, exhaustive understanding of geo-spatial and asset systems for mission planning, and data capture techniques. One example of this would be prioritizing the inspection and maintenance of field assets based on the asset meta data and real-time operational data from those assets. This data set, combined with third-party data sources (such as weather data), can convert a normal predictive maintenance schedule to an enterprise-wide, condition maintenance-based schedule. This can save time, effort, and money while improving asset life span.
Utility assets include existing transmission and distribution lines and a lot of new, widely distributed renewable generation. Poorly managed vegetation could wreak havoc on a good portion of these assets. In the past, utilities have managed vegetation based either on fixed schedules or as encroachment caused operational issues, i.e. when trees or branches touch wires or when trees fall on wires during storms. By managing vegetation proactively, utilities will be in a better position to reduce costly outages to improve reliability.
Falling trees and branches, especially during storms with snow and high wind speeds, are a major source of outages. Failures of conductors, towers, insulators and other outdoor devices can cause blackouts, brownouts, and efficiency loss when power is lost enroute from generation to loads.
TCS has developed technology that combines unstructured imagery from satellites, helicopters, drones, land vehicles, and human inspections using a variety of camera and LIDAR imaging technologies. Advances in LIDAR technologies developed for use in autonomous cars enable TCS to integrate this data with other imagery sources. Each imagery source has different costs, resolution, sample frequency, and technical limitations. Collecting and filtering imagery from multiple sources can help optimize use of low-cost methods and reduce the costs associated with collecting imagery at higher frequency. This imagery is organized on secure cloud computing platforms and coupled with data analytics that can assess the current and predicted state of utility transmission and distribution assets. The analytic models can be used to target the need for urgent maintenance and, in certain cases, the need for specific inspection to better determine appropriate 
TCS can also gather imagery from solar panels and wind turbines for inspection, monitoring, and identification. Imagery is integrated with GIS information and connected to enterprise asset management (EAM), field service management (FSM), work order systems and integrated with other operational technology systems.
The TCS-developed technologies and service models are designed to help utilities reduce outages and improve the efficiency of their renewable generation assets.
Capturing images and video using drones, helicopters, or humans on the ground generates a substantial volume of data. This is going to increase exponentially as the cost of capturing images and video decreases further. This makes a unified “data governance” framework critical to be able to manage the data lifecycle across an enterprise and extended partners at all levels: acquisition, storage, retrieval, processing, and retention. TCS has developed the platform needed to efficiently manage data and workflow in image analytics and capability. This enables utilities to label the image data obtained, in tandem with the geo-spatial 
A provision of the “Samhua” crowd-sourcing concept is also integrated with the image analytics solution. According to TCS, this helps generate and implement innovative ideas through collective intelligence and leveraging massive parallel processing.
Data acquisition systems for collecting imaging datasets are driven primarily by the business problem and associated operating environments. Data acquisition protocols are designed, developed, and deployed specifically to deliver high-quality data capture from the field. This includes defining the data source payload/sensors, expected quality and resolution of data, data capture strategy (e.g., using a drone), season, time of day, acceptable weather and climatic conditions, meta data requirements, and acquiring additional (existing) enterprise intelligence.
TCS has developed image analytics algorithms that process these datasets, which are typically built to work in tandem with the specific data acquisition protocol and vice versa. These two worlds – data acquisition and data processing algorithms – cannot exist in silos and strategies must factor in this aspect or risk being sub-optimal and fail to deliver the desired results. This is the driver behind TCS’ deployment of robust AI/ML-based algorithms intended to deliver high-accuracy results.
TCS also understands that while algorithms make processes more efficient, each problem statement has a unique need and organizational priority. Hence TCS subject matter experts (SME) are critical for both training the machine and monitoring performance.
The AI/ML algorithms require both the right training and associated testing cycles to ensure the desired accuracy and robustness. Training the AI and ML models requires the domain subject matter expert to provide the right inputs and annotations to help build the ground-truth reference data for subsequent auto annotation.
Model performance typically degrades over time. This is due primarily to new varieties of unseen data that would require retraining the model. To help ensure continued robustness, the model performance (accuracy/precision and recall metrics) must be monitored regularly by the subject matter expert.
Even with the increasing fraction of non-dispatchable renewable power generation in today’s electric grids, electric utilities must meet reliability targets. In North America, the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) develops and enforces mandatory grid reliability standards, which are approved by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC).
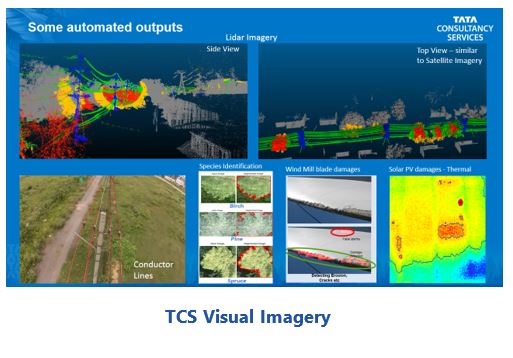
Infrared inspection of solar PV arrays can identify damaged panels that are not operating properly, since these will run hotter than panels that are performing properly. Drone imagery can help detect these temperature differences in less time than human inspections. It is important to detect changes/damages that can identify the locations of faults in combiners, inverters, and strings. This is achieved with 2D imagery (visual and infrared spectrum) and associated data from the system. This can reduce a two-day manual exercise to a 30-minute drone flight. This image- based analytics capability can keep solar PV generation operating at top performance for longer durations.
Different utilities across the world are at different stages of maturity when it comes to defining the use cases and developing and deploying image analytics technology. But, as we learned, TCS is leveraging its broad value chain to add value to the image analytics journey undertaken by multiple clients.
In vegetation management, TCS is helping utilities in Australia and North America automatically identify species from imagery, predict growth, and detect encroachment of vegetation on lines, towers, and other field assets. In asset management, TCS is leveraging its contextual knowledge and refined algorithms (AI/ML) to sort through thousands of images and video frames to quickly and automatically identify damaged assets. This has already been developed for a North American utility on the West Coast and is about to be piloted by another utility in Australia.
For utilities that have already procured petabytes of imagery for image analytics, TCS is deploying the data management platform to utilize the imagery effectively and integrate with other structured enterprise data sets. The company believes that this approach will be key in the future to help utilities adopt enhanced image analytics for prescriptive and predictive insights.
How can utilities make best use of imagery-derived data from multiple sources to improve asset management?
According to TCS, utility operators can now be provid
The trend in renewable generation indicates that wind and solar are the largest sources of new generation capacity for the US grid. These new assets require monitoring and maintenance. With the shift towards renewable generation, new transmission and distribution systems are being added and upgraded. The coming wave of EVs and increased electrification of HVAC mean that transmission and distribution changes will be required. Utilities already maintain fleets of drones, helicopters, and fixed wing aircraft that collect imagery of transmission lines and generation assets. Image management is a necessary part of managing utility assets.
Combining the drone-derived imagery with GIS location metadata allows tree species to be identified and, by integrating weather data, makes it possible to create models of vegetation growth. Analytics and machine learning can then be used to help utilities plan effective vegetation maintenance by integration with work order processing. For example, TCS is planning to add the ability to track and model wildfires accurately in real time to help improve both firefighting effectiveness and firefighter safety.
The TCS solutions for utility asset management coupled with the company’s established expertise in operational technology, provides valuable monitoring, operation, efficiency, and support for maintenance of many utility assets, including renewable generation assets.
ARC Advisory Group clients can view the complete report at ARC Client Portal
If you would like to buy this report or obtain information about how to become a client, please Contact Us
Keywords: Image Analytics, Satellite Imagery, LIDAR, Utility Asset Management, AI, ML, Operational Technology, Drones, ARC Advisory Group.

