

Industry 4.0 and its digitalization aligns with the methodologies of Lean Six Sigma to help accelerate continuous improvement. A kaizen team’s value stream map identifies real opportunities for improvement since no one understands the process better than the team members that do the work. Manufacturers should educate their workforce on Industry 4.0 technologies and support the kaizen teams in identifying practical applications. Sometimes, this could include a thorough re-evaluation of the entire map, such as when replacing paper-based processes with mobile solutions.
In 1978, Taiichi Ohno wrote his book on the Toyota Production System (TPS) (the term “Lean Manufacturing” was coined 13 years later). Considering the state of IT in 1978 with punch cards, weekly batch runs, and voluminous printed reports, it is no wonder that Ohno had a bias against technology. Obviously, technology has advanced a long way since then.
What impact does Industry 4.0 have on Lean Six Sigma programs? Lean manufacturing methodologies have been deeply internalized into the culture of most industrial companies since the 1990s. Typically, the program has an internal name and is modified slightly to fit the unique needs of a company’s business model and processes. Today, nearly all large and mid-size manufacturers worldwide have a corporate business improvement program based on lean six sigma. For sustained adoption, adding Industry 4.0 must occur in a way that aligns with the lean six sigma culture.
Lean and Six Sigma provide two compatible problem-solving methodologies. In both cases, people who do the actual work collaborate in a kaizen event (a team meeting). The team examines the process they are involved with to identify and implement improvements.
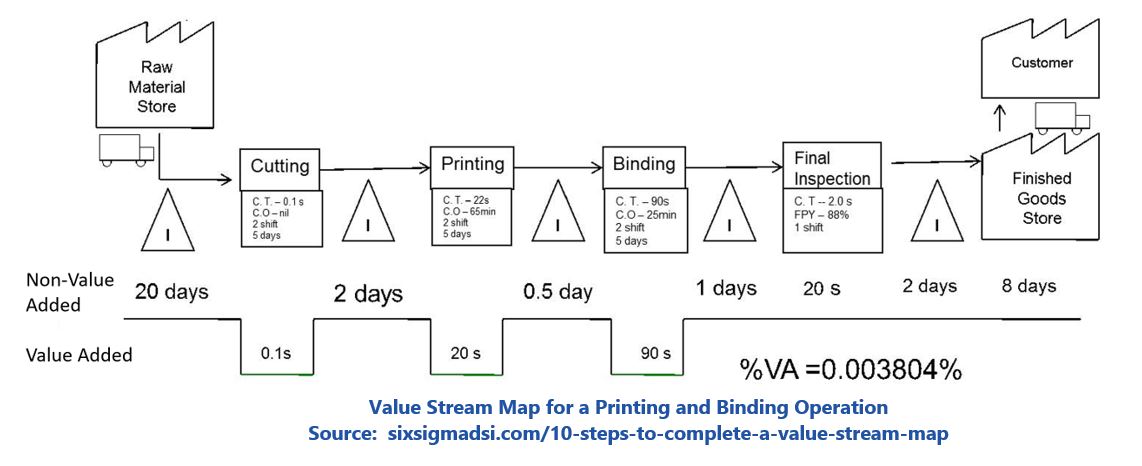
Put simply, lean typically starts with understanding the added-value for the customer, and then examining a process in detail using value stream mapping (VSM). Incremental improvements involve either eliminating waste (activities, delays, or resources) or incorporating newer technologies that didn’t exist when the process was established.
When the VSM identifies a quality issue in a process step, Six Sigma provides a methodology for data driven analysis to define and quantify the types of errors. Statistical analysis is used to identify root causes and implement process improvements that reduce the errors.
Continuous improvement is a process examining existing activities and processes to identify improvements. These changes can be considered organic in nature because they build on and optimize existing processes. Radical transformation involves creating new processes and new business models.
Like Lean, Industry 4.0 focuses on business processes. Industry 4.0 involves business process automation and data exchange using the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, analytics, machine learning and artificial intelligence. Some have broadened Industry 4.0 to include a variety of newer technologies including 3D scanning, additive manufacturing, blockchain, augmented reality, virtual reality, and drones.
Continuous: Usually, applying Industry 4.0-associated technologies dramatically improves an existing business process. Using VSM provides a higher rate of sustainable success. This includes digitalization, such as replacing paper-based procedures with a digital workflow and mobile devices.
Radical: Occasionally, Industry 4.0 and related technologies enable a more radical digital transformation or a new business model. An example of a new business model is equipment as a service. Rather than purchasing an asset, a company can rent it with a service-level agreement that employs condition monitoring using IoT and analytics for predictive maintenance.
Applying Industry 4.0 typically involves continuous types of improvement and, only occasionally, radical approaches. This report focuses on the continuous improvement.
Industry 4.0 includes data acquisition, analytics, and collaboration that enable faster consensus building among the kaizen event members and improved speed of execution. Kaizen teams are often thwarted by a lack of data for analysis that impedes collaboration and blocks progress – particularly with Six Sigma. Industry 4.0 involves technologies to overcome each of these impediments using:
Use VSM to identify practical applications of advanced technologies. After creating the “as is” version of the graphical map, the team looks to identify waste and eliminate it. Industry 4.0 adoption enables examination of the value stream map for process automation with the newer technologies mentioned previously. This VSM approach provides a repeatable methodology for evaluating and adopting technology with clear business benefit and user support.
ARC Advisory Group clients can view the complete report at ARC Client Portal
If you would like to buy this report or obtain information about how to become a client, please Contact Us
Keywords: Lean Six Sigma, Digitalization, Industry 4.0, Value Stream Map, ARC Advisory Group.

