

Artificial intelligence can be used in many different applications in machinery automation. In last year’s study, we identified the following applications where AI is already in use. To refine and update this information, we are currently running an online Artificial Intelligence for Machinery Applications Survey, and participants will receive a complimentary copy of the key findings. In 2019, we identified these key applications:
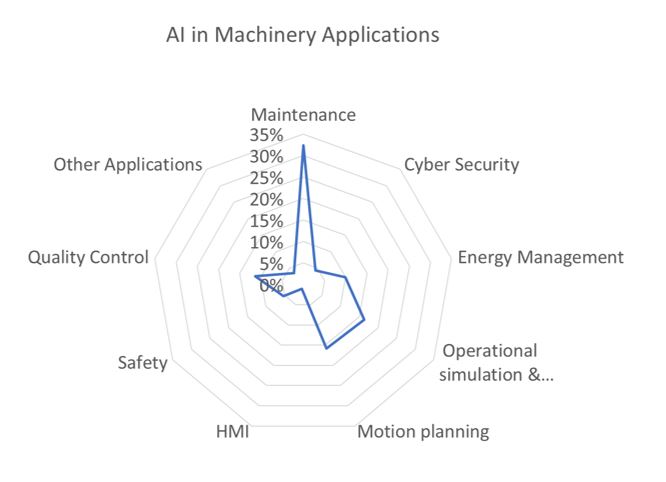
The chart shows the percent distribution in terms of the market. Maintenance is certainly among the hottest topics right now. There are multiple reasons for this:
Another area that has always been a priority two target for operators, but which can bring tremendous savings, is energy management. The aspect is probably slightly under-represented in our study, where we focus on machinery applications, and there are also many use cases on the MES and EAM level. Often energy usage is handled by the building management part and not directly at the machine level. Users can see many good results when an energy management system is integrated with manufacturing execution systems (MES), or even with enterprise asset management (EAM) systems. Thus, the energy data can be collected from the numerous appropriate meters or submeters, assets or processes across the plants that are even located remotely.
Accurate and reliable energy data, in conjunction with new web-based enterprise wide software and data analytics solutions are transforming the face of business and redefining entire industries’ processes at the asset level for achieving goals on energy savings, cost reductions, sustainability, carbon footprint, and productivity improvement. Even with these technology-enabled solutions in place, companies still need to develop internal processes to share and analyze the data and implement it across their organization.
In ARC’s point of view, AI can enable quick results in energy savings with limited costs and deliver sustainable savings to the end user. The data for energy consumption - including electricity, air, gas, water, or even nitrogen (for cooling) - can be measured easily and reliably. The patterns typically are foreseeable as well and include weather, production change, ramp up/down, leakage of pneumatics, etc., so the AI can be tailored towards them.
While energy management has been a priority two aspect for many users, there are some very illustrative examples on how AI is already used to lower energy consumption and the carbon footprint. We have these examples:

